CHAPTER 8: Microsoft 365 Security Features
 Welcome to Microsoft 365 Security Features. In this chapter, we are going to review a few key Microsoft 365 security features.
Welcome to Microsoft 365 Security Features. In this chapter, we are going to review a few key Microsoft 365 security features.
We will start things off by covering identity and access in Microsoft 365. We'll look at secure authentication solutions, conditional access, and identity protection.
Next, we’ll cover key threat protection solutions that Microsoft 365 offers. We'll review Azure Active Directory Identity Protection, Advanced Threat Protection, Azure Security Center, and a few others.
After covering the key threat protection solutions in Microsoft 365, we'll take a look at the Microsoft Security Center and the Secure Score.
Identity and access in Microsoft 365
Identity and access management is probably the most important security pillar in Microsoft 365. By offering secure authentication, Microsoft 365 helps you protect against account breaches. Conditional access that is offered by Microsoft 365 offers granular access to corporate data. Identity protection features in Microsoft 365 can be used to ensure hackers do not steal the identity of your users.
Let’s start things off by taking a look at how Microsoft 365 provides secure authentication.
Secure Authentication
Protecting your organization against breaches means you need to protect your users. Ensuring that your users use complex passwords is one way to protect them. However, such complex passwords can be difficult to remember - and because complex passwords are so difficult to remember, users will often just use the same complex password for all of their sites and resources.
Relying solely on complex passwords can also be problematic because no matter how complex the passwords are, they are subject to replay attacks and they are often exposed due to phishing attacks. This obviously presents challenging security risks, especially since most breaches originate with compromised passwords.
To help reduce the risks associated with passwords, Microsoft 365 offers a few replacement options. These options include Multi-Factor Authentication, Windows Hello, and Microsoft Authenticator.
Multi-Factor Authentication, or MFA, allows you to specify multiple factors for authentication. It forces users to provide at least two authentication factors to identify themselves. These factors typically consist of something the user knows, such as a password or pin, something the user has, which would often be a smart card or digital certificate or even a phone, and it’s something the user is, which is usually some sort of biometrics.
Windows Hello is a Windows 10 feature that replaces passwords with two factor authentication on both PCs and mobile devices. This is a newer type of user credential that gets tied to a specific device and leverages either a pin or some form of biometric. Users can use Windows Hello to authenticate in Active Directory and in Azure Active Directory.
Microsoft Authenticator is an application that organizations can use to keep accounts secure. It works by offering two factor verification and phone sign in. Two factor verification is the standard verification method. The first factor is the user’s password. However, once a user signs into a device, app, or site, using his username and password, the user must use Microsoft Authenticator to either approve a notification or answer a verification code that is provided.
The phone sign-in option is another version of two factor verification that allows users to sign in without a password. Instead of using a username and password combination, users can login with a username and a mobile device with a fingerprint, face, or pin.
Conditional Access
Conditional access allows organizations to provide granular access to data and applications. It allows users to work from virtually any location and from just about any device. Conditional Access evaluates users, devices, apps, location, and risk before granting a specific user access to a corporate resource. This ensures that only those approved users can access company resources from only approved devices.
 Conditional Access evaluates access requests against several different criteria. It then compares this criterion to policies that you define. After comparing against these policies, Conditional Access will decide whether or not access is allowed.
Conditional Access evaluates access requests against several different criteria. It then compares this criterion to policies that you define. After comparing against these policies, Conditional Access will decide whether or not access is allowed.
I should mention that Conditional Access spans multiple Microsoft 365 services including Office 365, Windows 10, and InTune.
Identity Protection
Because most security breaches occur as a result of stolen user identities, identity protection is critical. Not only do you need to protect all of your user identities from being compromised, but you also need to ensure that you are proactively preventing compromised identities from being abused.
Microsoft 365 offers several ways for organizations to protect their identities. They include Azure Active Directory Identity Protection, Microsoft Cloud App Security, Azure Advanced Threat Protection, and Windows 10’s built-in identity protection capabilities.
Azure Active Directory Identity Protection helps organizations identify attempts to compromise user accounts. Whenever it identifies unusual behavior from an account, Azure Active Directory Identity Protection can block access and even require additional authentication options.
Microsoft Cloud App Security provides analytics for cloud apps and services. This helps organizations understand protections that are in place for their data across cloud apps.

Azure Advanced Threat Protection, or ATP, is a cloud-based security solution. Using ATP, organizations can identify, detect, and investigate many different threats, compromised identities, and other malicious activity that’s directed at the organization.
The built-in identity protection capabilities of Windows 10, including Windows Hello, can be used to further protect user identities.
So, as you can see by providing secure authentication, conditional access, and identity protection features, Microsoft 365 helps organizations manage the first security pillar which is identity and access management by helping them identify who is accessing resources and helping them control what can be accessed.
Threat Protection in Microsoft 365
Organizations that leverage Azure Active Directory get the benefits of the adaptive machine learning algorithms that it uses to detect suspicious incidents and identities that may be compromised. This data is used by Azure Active Directory Identity Protection to create reports and alerts that you can use to evaluate potential security issues and take action.
In addition to monitoring and reporting, Azure Active Directory Identity Protection allows you to configure risk-based policies that will automatically respond to suspicious incidents that are detected. These policies can be used with conditional access controls to automatically block access and to even automatically take remediation actions.
Azure Advanced Threat Protection
Azure Advanced Threat Protection, or ATP, is a cloud-based security solution. What Azure Advanced Threat Protection does is identify and detect advanced threats, compromised identities, and certain malicious insider actions. The security reports and analytics that ATP offers are useful for reducing your organizations attack surface.
Azure Security Center
Azure Security Center is another security tool. It offers advanced threat protection and unified security management across hybrid cloud workloads, which include those workloads on-prem, in the Azure cloud, and in other clouds. Azure Security Center will even allow you to automatically discover and onboard new Azure resources. Defined security policies are automatically applied to ensure such new resources are compliant with your security standards. You can use Azure Security Center to collect and analyze security data from many different sources, including firewalls and even partner solutions.

Microsoft Exchange Online Protection
The Microsoft Exchange Online Protection service, or EOP, is a cloud-based email filtering service provided to Microsoft exchange online customers. This anti-spam and antimalware solution provides email protection.
Microsoft InTune
Microsoft InTune is a mobile device management solution that is part of enterprise mobility and security, or EMS. It integrates with other EMS components as well. For example, its integration with Azure Active Directory helps provide identity and access control, while its integration with Azure information protection helps secure data. Using Microsoft InTune with office 365 can help protect your data while allowing users to work from virtually any device.
Office 365 Advanced Threat Protection
Office 365 Advanced Threat Protection is a security offering that is included in Microsoft 365 E5 subscriptions. It is used to identify threats before they make their way into a user’s mailbox by scanning email and URLs, identifying and blocking malicious files, and detecting impersonation attempts. The safe links feature of Office 365 Advanced Threat Protection scans emails in real time. Users are presented with a warning message if they click on a link that may be malicious. Attack Simulator, which comes with Advanced Threat Protection, can be used to simulate realistic attacks as well.
Office 365 Threat Intelligence
Office 365 Threat Intelligence consists of insights and other information - and is available in the Office 365 Security and Compliance Center. This tool can be used to understand different threats against your users and data because it monitors different signals and gathers data from several different sources, including email, compromised PCs, user activity, and other security incidents.
By leveraging these many different security tools, you can protect your users, identities, devices, user data, apps, and infrastructure.
Microsoft 365 Security Center and the Secure Score
 The Microsoft Security Center is used to track and manage security for identities, data, devices, apps, and even infrastructure. Security Center will generate alerts when suspicious activities are identified. The real-time reports that Microsoft Security Center offers allow organizations to keep track of issues within their organization. Because it provides many different insights and recommendations, the Microsoft Security Center can help organizations improve their security posture. You can even use the security Center to configure device and data policies.
The Microsoft Security Center is used to track and manage security for identities, data, devices, apps, and even infrastructure. Security Center will generate alerts when suspicious activities are identified. The real-time reports that Microsoft Security Center offers allow organizations to keep track of issues within their organization. Because it provides many different insights and recommendations, the Microsoft Security Center can help organizations improve their security posture. You can even use the security Center to configure device and data policies.
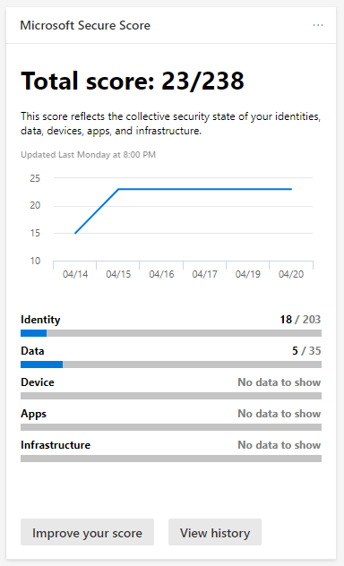
Within the Microsoft Security Center, you’ll find the Microsoft Secure Score. The Secure Score is a configurable security score assigned to your environment. This score provides an overall view of your security posture. You can use the centralized dashboard to not only monitor the security of your environment, but you can also use it to improve that security.
The Microsoft Secure Score offers detailed data visualization as well as integration with other Microsoft products. You can even use it to compare your score with other companies. By completing the improvement actions that are called out, you can improve your score and harden your environment.
The way that the Secure Score works is rather straightforward. It assigns points whenever you configure its recommended security features and when you perform certain security related tasks. It also assigns points for addressing certain improvement actions. The idea is to get your Secure Score as high as you can, while balancing the security and usability in your environment, because some recommendations won’t necessarily work in your environment, given how you do business.
Ultimately, what you want to do is use the Microsoft Secure Score recommendations to identify the most important settings to you and to make changes that you deem necessary.
What You’ve Learned
Congratulations! You’ve reached the end of Microsoft 365 Security Features. Let’s review what you’ve learned.
We started things off by covering identity and access in Microsoft 365, where we looked at secure authentication solutions, conditional access, and identity protection.
Next, we covered the key threat protection solutions that Microsoft 365 offers. We reviewed Azure Active Directory Identity Protection, Advanced Threat Protection, Azure Security Center, and a few others.
After covering the key threat protection solutions in Microsoft 365, we looked at the Microsoft Security Center and the Secure Score.
Prefer the PDF version? No problem.
Click here to download the full 89-page PDF version of this guide for just $2.99.
As an added BONUS, I've included 30 Microsoft 365 practice questions in the PDF version.
Prefer the full 3-hour online course? Click here to enroll in the full course.
About the author